Bone Cement
Bone cements for orthopedic, with antibiotics, are self-curing, radiopaque, polymethyl methacrylate-based cements used for securing a metal or polymeric prosthesis to living bone in arthroplasty procedures, such as hip replacement, knee replacement, and other joint replacements, and are specifically formulated for patients.
| G1 40 | G1A 40 |
|---|---|
| Radiopaque Bone Cement | Radiopaque Bone Cement With Antibiotic |
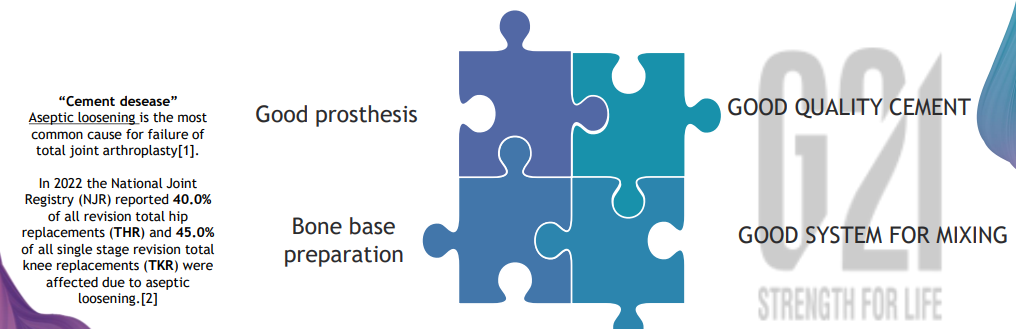
Orthopaedic bone cements today - Why it is important?
Bone cement plays a crucial role in filling the space between irregular bone and the smooth surface of the prosthesis, ensuring even load distribution. Since aseptic loosening is the most common cause of total joint arthroplasty failure, the importance of bone cement in maintaining implant stability cannot be overstated.
“The orthopedic bone cement G1A adopted in arthroplasty implants has shown optimal capacity of fixation of the prosthetic implant with no evident area of bone per prosthetic suffering.” [1]
[1] Report clinical and radiologic study on patients undergone total knee prosthesis cemented with G1A. 2017- Dr. Castellarin
Downloads
View moreContact Us
"*" indicates required fields
Why Shalby MedTech
We are committed to deliver solutions and transforming the way joint replacement procedures are performed.
 Reliability
Reliability
 Integrity
Integrity
 Teamwork
Teamwork

 Looking for the
Looking for the  Register as
Register as